Loops are fundamental to programming, and PHP loops are no exception. Whether you’re iterating over arrays or executing a block of code multiple times, loops are essential for writing efficient and clean PHP code. This guide covers every PHP loop type, for, while, do while, and foreach, with clear explanations and working examples to help you understand how and when to use them.
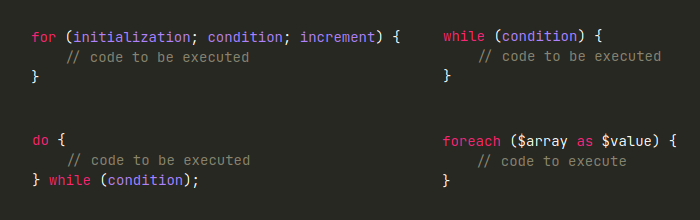
Table of Contents
Why Use PHP Loops?
In any real-world application, repetitive tasks are common. Rather than writing repetitive code, loops allow you to automate such tasks efficiently. All PHP loops follow this general principle: execute a block of code multiple times until a specified condition is met or fails.
PHP Loops 1: The For Loop in PHP
The for loop is ideal when you know in advance how many times a block of code should run. A loop variable is initialized to a start value which is often set to zero. This is the initialization in the code below.
A condition is checked each time through the loop – this is the condition in the code below. Code in the loop body is run if the condition evaluates to true. If the condition evaluates to false, then the loop is exited.
After running the code in the loop, the loop variable is incremented according to the increment value in the code below. Alternatively, the loop variable can be decremented here if desired.
Syntax:
for (initialization; condition; increment) {
// code to be executed
}Example:
for ($i = 0; $i < 5; $i++) {
echo "Number: $i<br>";
}In this example, the loop starts at 0 (initialization: $i = 0) and runs while $i is less than 5 (condition: $i < 5), incrementing by 1 each time (increment: $i++). Five numbers are output, but because the first number is zero, the five numbers are 0 to 4 instead of 1 to 5 in this example.
Output in the Browser:
Number: 0
Number: 1
Number: 2
Number: 3
Number: 4Output HTML Code:
Number: 0<br>Number: 1<br>Number: 2<br>Number: 3<br>Number: 4<br>PHP Loops 2: PHP While Loop
A PHP while loop executes code as long as the condition evaluates to true.
Syntax:
while (condition) {
// code to be executed
}Example:
$i = 0;
while ($i < 5) {
echo "While Loop Number: $i<br>";
$i++;
}This loop works well when the number of iterations isn’t known upfront. In the above example, the loop variable $i is initialized to zero before reaching the loop. When the loop is reached, the loop condition ($i < 5) is evaluated. If this expression evaluates to true, if $i is less than five in this example, then the code in the loop body is run. On the other hand, if the loop expression evaluates to false, then the code in the loop body is skipped over and not run.
The last line of code in this example increments the loop variable. After this the loop expression is evaluated again. Once again, if it evaluates to true, then the loop code is run. If it evaluates to false, the loop is exited.
Output in the Browser:
While Loop Number: 0
While Loop Number: 1
While Loop Number: 2
While Loop Number: 3
While Loop Number: 4Output HTML Code:
Number: 0<br>Number: 1<br>Number: 2<br>Number: 3<br>Number: 4<br>PHP Loops 3: PHP Do While Loop
A PHP do while loop is similar to the while loop, but it guarantees that the block of code runs at least once, even if the condition is false.
Syntax:
do {
// code to be executed
} while (condition);Example:
$i = 0;
do {
echo "Do While Number: $i<br>";
$i++;
} while ($i < 5);This type of loop is useful when you need to execute code first and then test the condition. The above code works exactly the same as the previously explained while loop, except that the code in the body of the loop is run first, and then the condition expression is evaluated last. If this expression evaluates to true, then the code in the loop is run again. On the other hand, if the loop expression evaluates to false, then the loop is exited.
Output in the Browser:
Do While Number: 0
Do While Number: 1
Do While Number: 2
Do While Number: 3
Do While Number: 4Output HTML Code:
Do While Number: 0<br>Do While Number: 1<br>Do While Number: 2<br>Do While Number: 3<br>Do While Number: 4<br>PHP Loops 4: Foreach in PHP
When dealing with arrays or objects, foreach in PHP is the most efficient loop to use.
Getting Single Values from an Array
Read single values from an array with the foreach loop in the following way.
Syntax:
foreach ($array as $value) {
// code to execute
}Example:
$fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry'];
foreach ($fruits as $fruit) {
echo "Fruit: $fruit<br>";
}In the above code, $fruit takes on the current value from the $fruits array. As the foreach loop loops through the array from start to end, the current value depends on how far the loop has gone through the array. In this example, the first time or iteration through the loop, $fruit takes on the first value in the array which is ‘Apple’. The second time through the loop, $fruit takes on the value ‘Banana’. The third and final time through the loop, $fruit takes on the value ‘Cherry’.
Output in the Browser:
Fruit: Apple
Fruit: Banana
Fruit: CherryOutput HTML Code:
Fruit: Apple<br>Fruit: Banana<br>Fruit: Cherry<br>Getting Key Value Pairs from an Array
You can also use key-value pairs in a foreach loop:
$users = ['Alice' => 25, 'Bob' => 30];
foreach ($users as $name => $age) {
echo "$name is $age years old<br>";
}In the above code, the foreach loop loops through each name (or key) value pair in the array from the start of the array to the end of the array. Each time through this PHP loop, $name takes on the name string from the array, and $age takes on the corresponding value from the array.
Output in the Browser:
Alice is 25 years old
Bob is 30 years oldOutput HTML Code:
Alice is 25 years old<br>Bob is 30 years old<br>Choosing the Right PHP Loop
| Loop Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
for | Known number of iterations |
while | Unknown number, condition evaluated before |
do while | Unknown number, run at least once |
foreach | Best for arrays and associative data structures |
Understanding each PHP loop helps you select the best one for your task, improving code clarity and performance.
Alternatives to PHP Loops: Functional and Advanced Constructs
While PHP officially provides only four types of loops (for, while, do while, and foreach), there are other constructs that can perform similar tasks. These alternatives are particularly useful for developers who prefer a more functional or modern programming style. Each of these alternative is discussed in the sub-sections that follow.
Using array_map() Instead of PHP Loops
The array_map() function in PHP behaves much like the map() function in Python. It applies a callback function to each element of an array, returning a new array with the transformed values.
Example:
$numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
$squared = array_map(fn($n) => $n * $n, $numbers);
print_r($squared);
// Output: [1, 4, 9, 16]
This provides a concise alternative to foreach in PHP when transforming arrays.
Filtering and Reducing Arrays
Two other useful functions are array_filter() and array_reduce():
array_filter(): Filters elements based on a condition.array_reduce(): Reduces an array to a single value using a callback.
Example using array_reduce():
$nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
$sum = array_reduce($nums, fn($carry, $item) => $carry + $item, 0);
echo $sum;
// Output: 15
These functions are excellent for concise and expressive data operations without manual looping.
Generators and the yield Keyword
PHP also supports generators, which allow you to define custom iterators using the yield keyword. Generators are memory-efficient and especially useful for large datasets.
Example:
function generateRange($max) {
for ($i = 0; $i < $max; $i++) {
yield $i;
}
}
foreach (generateRange(3) as $num) {
echo $num . "<br>";
}
// Output: 0<br>1<br>2<br>
This pattern gives you fine control over iteration without creating large arrays.
Recursion as a Loop Replacement
Although less common due to PHP’s stack limitations, recursion can also replace certain types of loops.
Example:
function countdown($n) {
if ($n <= 0) return;
echo "$n<br>";
countdown($n - 1);
}
countdown(3);
// Output: 3<br>2<br>1<br>
Use recursion carefully, as deeply nested calls can lead to stack overflow in PHP.
These alternatives to standard PHP loops are not direct substitutes for every use case, but they offer powerful and expressive tools when working with collections, sequences, or complex data transformations.
FAQs About PHP Loops
What’s the difference between while and do while in PHP?
The while loop checks the condition before the first iteration, while the do while loop checks the condition after running the code at least once.
Can I break out of a loop in PHP?
Yes, use the break statement to exit a loop prematurely, and continue to skip the current iteration.
When should I use foreach instead of for?
Use foreach in PHP when iterating over arrays or objects, as it’s cleaner and more readable.
Conclusion
Mastering all PHP loops is crucial for effective programming. From the classic for loop to the array-friendly foreach in PHP, each loop serves a specific use case. By understanding when and how to use each loop type, including php while loop and php do while, you’ll write cleaner and more efficient code.
For more PHP tips and real-world coding examples, explore our full library under the PHP category on Programmer Notes.
References
1. PHP for loop reference: https://www.php.net/manual/en/control-structures.for.php
2. PHP while loop reference: https://www.php.net/manual/en/control-structures.while.php
3. PHP do while loop reference: https://www.php.net/manual/en/control-structures.do.while.php
4. PHP foreach loop reference: https://www.php.net/manual/en/control-structures.foreach.php
