Understanding how to use and in Python is crucial for writing effective conditional logic. The and keyword lets you combine multiple conditions into a single boolean expression, often seen in if statements and while loops. This is a core concept in control flow and decision-making in Python programming.
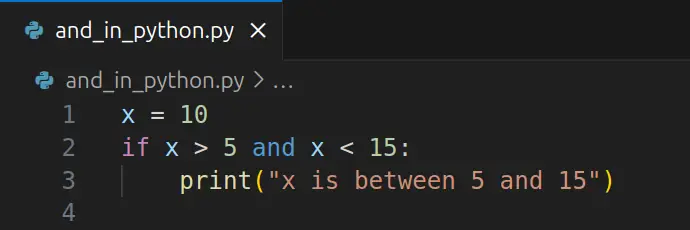
Table of Contents
Syntax and Meaning of and in Python
In Python, and is a logical operator used to evaluate two expressions. If both expressions evaluate to True, the entire statement is True; otherwise, it returns False.
Basic Example
x = 10
if x > 5 and x < 15:
print("x is between 5 and 15")Here, x > 5 and x < 15 is a compound condition. Since both parts are true, the message is printed.
This simple pattern, if with and in Python, one of the most common use cases for compound conditions.
Using and in Python if Statements
When writing complex conditions, Python if and patterns help combine multiple checks into one logical unit. This makes your code more readable and avoids deeply nested if statements.
Example: Multiple Conditions with if and
user = "admin"
authenticated = True
if user == "admin" and authenticated:
print("Access granted")In this if and statement, Python checks both conditions. If either one fails, the block will not execute.
Alternative Syntax: and Python if Variants
Variants of and Python if statements can be used with logic checks: Python evaluates each condition from left to right and stops as soon as it can determine the outcome (short-circuit evaluation).
Short-Circuiting Example
def is_valid():
print("Checking validity...")
return False
if False and is_valid():
print("Won't print")
In this case, is_valid() is never called because the first condition is False, and and short-circuits the evaluation.
The if and Statement in Python: Best Practices
The if and statement in Python becomes more readable when broken across lines using parentheses:
age = 25
has_id = True
is_sober = True
if (age >= 21 and
has_id and
is_sober):
print("You may enter.")
This format is helpful for long conditions and avoids unnecessary nesting or repetition.
Using and in Python while Loops
The python while and combination is used when a loop must continue running only if multiple conditions remain true.
Example: while with and in Python
count = 0
limit = 5
running = True
while count < limit and running:
print(f"Count is {count}")
count += 1
if count == 3:
running = False
In this python while and structure, the loop exits early because one of the conditions becomes False.
Common Mistakes with and in Python
- Misplacing parentheses
Python doesn’t require parentheses forandconditions, but adding them incorrectly can change logic. - Using
&instead ofand
The&operator is a bitwise operator, not logical. Useandfor boolean expressions. - Assuming all conditions are checked
Due to short-circuiting, not all expressions may run. This can impact function calls inside conditions.
FAQ: Using and in Python
Can I use multiple and operators in one statement?
Yes. Python supports chaining multiple conditions using and. For example:
if a and b and c:
pass
Is and evaluated before or?
Yes. Python’s operator precedence gives and higher priority than or.
What’s the difference between and and &?
and is used for boolean logic, while & performs bitwise operations. Do not use them interchangeably.
Can I use and in ternary expressions?
Not directly. Use the ternary syntax:
result = x if condition1 and condition2 else y
Conclusion
Mastering how to use and in Python is essential for writing clear, concise, and effective logic. Whether you’re combining conditions in an if statement or managing control flow in a while loop, the and operator is a fundamental tool. Keep your conditions readable, watch out for short-circuiting, and avoid common mistakes for best results.
To explore more Python tutorials and deepen your understanding, check out the full collection on Python Programming.
